Our goal is to purchase 100% Green Energy for 100% of our clients.
Our goal is to purchase 100% Green Energy for 100% of our clients.

Energy buying doesn’t have to be complicated. We get to know your business, spot the best market opportunities, and create a simple, tailored plan , handling everything to secure maximum savings. Fast, clear, and stress-free.

The group purchasing program gives individual clients improved purchasing power. This enables them to receive a better wholesale market price for their energy while also receiving a wider range of terms and services from the supplier.

Reverse energy auctioning is an effective way for suppliers to reduce their margins and offer more competitive rates. Watch prices drop as the energy suppliers bid for your business.

We all want to be greener, and with Green Energy Tariffs now as competitive as standard ones, there’s never been a better time to make the switch. Request for a green tariff to compare.
We don’t simply collect prices. Instead, we work with a panel of trusted suppliers to give you real choice. We then encourage them to compete for your business by sharing comparative pricing and, whenever possible, running an online auction. This process drives down margins and helps secure the best possible value for you.
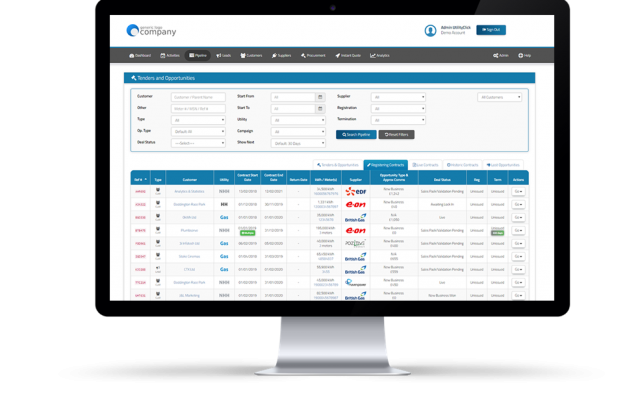
A large panel of trusted suppliers to bid on your business energy contracts.
Let suppliers bid for your business with an online reverse auction.
Quotations & contracts are compared and accepted online.
Over the years, we’ve built strong, long-standing relationships with a carefully selected panel of trusted suppliers. Each partner has been chosen for their commitment to quality, competitive pricing, and exceptional customer service. These relationships allow us to deliver reliable products, consistent value, and a seamless experience for our customers.












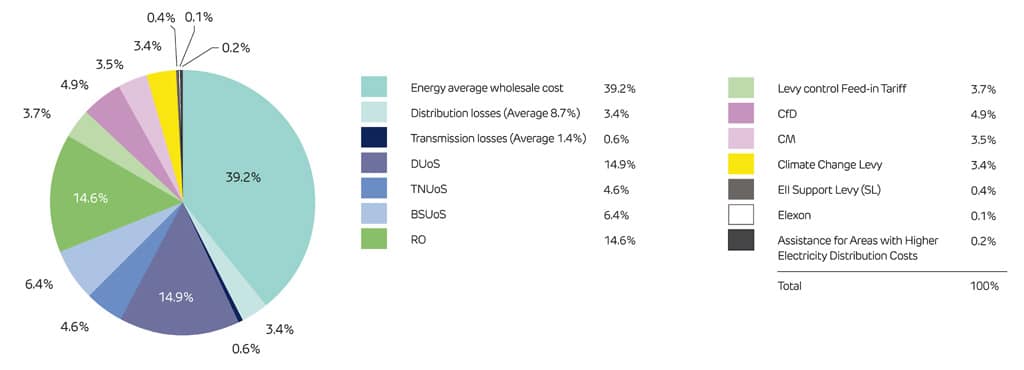
Business energy prices are split into two main components: Commodity Costs – the wholesale electricity price. Non-Commodity (TPC) Costs – all the charges listed above. Non-commodity costs can make up over 60% of a total electricity bill for many businesses. Suppliers may either: Pass these through transparently (itemised on the bill), or Include them within a fixed price (bundled into the unit rate).
Understanding the true cost of energy tariffs can be confusing, so we’ve broken it down to make it easier to understand.
This guide explains the key charges and what they mean for your energy bills.
Commodity costs represent the wholesale price of the energy purchased on the market. These costs fluctuate daily based on supply, demand, generation levels, and global market conditions.
Wholesale gas and electricity refers to the cost of buying in bulk from power generators or gas storage before it is delivered to businesses. These prices are influenced by factors such as fuel prices, weather patterns, renewable generation levels, network constraints, and market trading activity. Because wholesale prices can rise or fall rapidly, they play a major role in determining the final rate that commercial customers pay.
Non-commodity charges, including network fees and government policy costs, can represent more than 60% of a business electricity bill ( see above graph ) . Suppliers will either show these costs separately (pass-through) or combine them into a single fixed unit rate for ease.
DUoS charges cover the cost of transporting electricity through the local distribution networks owned and operated by Distribution Network Operators (DNOs). These fees contribute to the maintenance, operation, and ongoing upgrade of the network to ensure power is safely and reliably delivered to end users.
TUoS or TNUoS charges cover the cost of transporting electricity across the high-voltage national transmission network before it reaches local distribution systems. These fees fund the operation, maintenance, and development of the transmission grid, ensuring the secure and reliable flow of power across the country. Charges are set by the National Grid and apply to all electricity users.
Balancing Services Use of System Reflects costs incurred by National Grid ESO to balance supply and demand in real time. Includes reserve generation, constraint management, and frequency control. National Grid ESO
Elexon Balancing and Settlement Administration Cost of operating the Balancing and Settlement Code (BSC), which ensures all energy traded matches what’s consumed.
The CfD scheme is designed to encourage investment in clean, renewable energy. It provides low-carbon generators—such as wind, solar, and biomass—with long-term price certainty. If the wholesale market price is below the agreed strike price, the generator receives a top-up funded by electricity consumers through the CfD levy. This helps reduce carbon emissions and supports the transition to a greener energy system.
The Capacity Market is a government scheme designed to maintain a reliable electricity supply. It provides payments to generators and demand-response providers in return for committing to be available when the grid is under stress—typically during peak demand or system shortages. These “capacity providers” support overall system resilience and reduce the risk of blackouts.
The RO scheme supports large-scale renewable electricity projects across the UK. Renewable generators earn Renewables Obligation Certificates (ROCs) for every unit of green electricity they produce. Electricity suppliers must buy enough ROCs each year to meet their obligation or pay a penalty fee. The funds collected help drive investment in clean energy and reduce carbon emissions. These costs form part of all business electricity bills.
FiT is a government scheme designed to support small-scale renewable energy generation. Owners of solar panels, wind turbines, and other eligible technologies receive payments for every unit of electricity they generate, as well as additional payments for any electricity exported to the grid. This incentivizes clean energy production at a local level while contributing to the overall transition to a low-carbon energy system.
The EII scheme gives financial relief to businesses in energy-intensive sectors, such as manufacturing and heavy industry, by reducing certain non-commodity electricity charges. This support helps high-energy-use businesses stay competitive in global markets while continuing to meet sustainability and energy efficiency goals.
The CCL is a tax applied to electricity, gas, and other forms of energy used by businesses, aiming to promote energy efficiency and support the UK’s carbon reduction targets. Some energy-intensive industries may qualify for exemptions or reductions under schemes such as the EII. The levy forms part of the non-commodity costs on commercial electricity bills.
Suppliers or customers offer us the “best price ” we can do this work on the clients behalf. We then use the “best price” as a bench mark and filter out the top 5 suppliers on price and terms . We then offer each supplier the opportunity to view an online auction and interaction with the quoting process. Suppliers bidding for the business rather than suppliers.
A group purchasing program gives individual clients improved purchasing power. This enables them to receive a better wholesale market price for their energy while also receiving a wider range of services from the supplier. Being part of a group like this can also provide benefits such as negotiating 100% Green Energy contracts at a cost neutral rate compared to Brown Energy. As a result Corporate Social Responsibility is improved.
Pass-Through contracts have a fixed price for the wholesale energy. However, any third party charges from the government are passed straight through to the customer. Suppliers pass the charges on instead of building them into the unit rate. These contracts can be cheaper than a fully fixed contract but carry the risk of charges increasing and the overall price going up.
Fully-Fixed energy contracts offer customers absolute budget certainty. All government and third party charges are built into the unit rate which remains the same throughout the length of the contract. This offers a level of security and certainty to clients who like to budget in advance.
Some Energy Suppliers offer contracts that can have an element of flexibility. Once the contract has started and been live for the required initial period we can ask for a “Blend and Extend Price“ should the energy market see a significant decrease. Increasing the length of a contract by another 12 or 24 months in these circumstances means we can secure cheaper prices. This allows the client to benefit from a falling market.
We actively encourage our clients to become more environmentally friendly by going green. This can offer a positive effect for their businesses in many ways. This includes helping to fight climate change as well as showing business commitment to helping the environment.
Suppliers or customers offer us the “best price ” we can do this work on the clients behalf. We then use the “best price” as a bench mark and filter out the top 5 suppliers on price and terms . We then offer each supplier the opportunity to view an online auction and interaction with the quoting process. Suppliers bidding for the business rather than suppliers.


